co2 electronic geometry|lewis dot structure for co2 : Manila One needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure helps in knowing the arrangement of electrons in the molecules and the shape of the molecule. To know the lewis . Tingnan ang higit pa *Seneca Gaming and Entertainment reserves the right to modify or discontinue this promotion without prior notice and is not responsible for typographical errors* Sun 1 August 1 @ 10:30 am - September 29 @ 8:00 pm
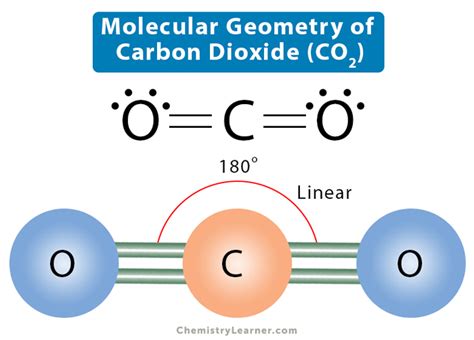
co2 electronic geometry,The molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central . Tingnan ang higit pa
One needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure helps in knowing the arrangement of electrons in the molecules and the shape of the molecule. To know the lewis . Tingnan ang higit paThe electronic configuration of the Carbon atom in its ground state is 1s22s22p2, and that of an Oxygen atom is 1s22s2p4. When the electrons are in an excited state, they jump to other orbitals. In its excited state, the atom’s electronic configuration becomes . Tingnan ang higit pa In this video we look at the electron geometry for CO2 (Carbon Dioxide). Because the Carbon dioxide molecule has two electron domains (two oxygen atoms and no lone pairs) the .
Determine the Electron geometry from the Lewis dot structure. Determine the molecular geometry. It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry .

According to the octet rule, an atom attains stability by fulfilling its octet. For example, in CO2, carbon needs 6 electrons to fulfill the octet, whereas oxygen needs . In its electronic ground state, the carbon dioxide molecule has a linear geometry (Fig. 7.1) and belongs to the point group D ∞h. Both C-O bonds are .co2 electronic geometry lewis dot structure for co2 CO2 Molecular Geometry & Shape. In a CO2 molecule, the carbon atom is in the center double bonded with two oxygen atoms by each side. Both oxygen atoms have two lone pairs of nonbonding . Carbon dioxide is therefore linear in electron-group geometry and in molecular geometry. The shape of CO 2 is linear because there are no lone pairs . Learn how to determine the electron and molecular geometry of CO2 with this easy and clear explanation video.The basic aspects of the reactivity of carbon dioxide (CO 2) are featured in this chapter and related to the electronic structure of the molecule. The electronic properties of neutral .lewis dot structure for co2CO2 Geometry and Hybridization. First, we need to draw the Lewis structure of CO 2. In short, these are the steps you need to follow for drawing a Lewis structure: 1. Write the .
Learn how to determine the electron and molecular geometry of CO2 with this easy and clear explanation video. Figure 5.9.5 5.9. 5: (a) The electron-pair geometry for the ammonia molecule is tetrahedral with one lone pair and three single bonds. (b) The trigonal pyramidal molecular structure is determined .Carbon dioxide has two electron groups and no lone pairs. Carbon dioxide is therefore linear in electron-group geometry and in molecular geometry. The shape of CO 2 is linear because there are no lone pairs affecting the orientation of the molecule. Therefore, the linear orientation minimizes the repulsion forces.Step 1. Find the point group of the molecule and assign Cartesian coordinates so that z is the principal axis. The CO 2 molecule is linear and its point group is D∞h. The z axis is collinear with the C∞ axis. We will use the D2h point group as a substitute since the orbital symmetries are retained in the D2h point group.The CO2 molecular geometry and bond angles notes conclude that the CO2 or carbon dioxide contains a total of 16 valence electrons which show on the outer shell of atoms, ie, four atoms of the carbon as well as 12 of two atoms of oxygen. With this, we can effortlessly draw the diagram of the Lewis dot of CO2 by adjusting two double bonds amid . Figure 7.6.9. Thus, the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular structure is bent with an angle slightly less than 109.5°. In fact, the bond angle is 104.5°. Figure 7.6.9: (a) H 2 O has four regions of electron density around the central atom, so it has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry.Example 5.2.1 5.2. 1: Predicting Electron-pair Geometry and Molecular Structure. Predict the electron-pair geometry and molecular structure for each of the following: carbon dioxide, CO 2, a molecule produced by the combustion of fossil fuels. boron trichloride, BCl 3, an important industrial chemical. Count the number of electron groups around each carbon, recognizing that in the VSEPR model, a multiple bond counts as a single group. Use Figure 9.3 to determine the molecular geometry around each carbon atom and then deduce the structure of the molecule as a whole. Solution:
co2 electronic geometry|lewis dot structure for co2
PH0 · valence electrons in co2
PH1 · lewis dot structure for co2
PH2 · electron geometry vs molecular geometry
PH3 · electron geometry chart
PH4 · co2 molecular geometry
PH5 · co2 electron pair geometry
PH6 · co2 electron domains
PH7 · c2h4 electron pair geometry
PH8 · Iba pa